The Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) highlights PFM reform momentum in Africa
By: Doug Hadden, Executive Vice President, Strategy and Innovation
You can be forgiven for thinking that public finance reform progresses slowly in emerging economies. My sense is that the combination of reform fatigue, with practice change inertia, adds friction to good intentions. There is only so much reform that public servants can absorb. Gaps between legal reform and informal practices widen, and best practice public financial management (PFM) laws become partly implemented, at best.
Recent sustainability initiatives promise to overcome PFM reform inertia. Sustainability is highlighted in the recent ACCA publication, PFM Performance in Africa and featured in the ACCA Virtual Africa Public Sector Conference (AVPSC2024) a few weeks ago. In his foreword to the publication, ACCA’s Director for Africa, Jamil Ampomah, suggests that “while public financial management (PFM) in Africa has significantly evolved over the last decades, the pace of reform continues to be challenged by systemic issues and deficiencies that undermine major investments from governments and development partners.”
How does sustainability lead to a shared PFM reform mission?
Notions of sustainability and support for the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) seem abstract in many advanced economies. Yet the lack of sustainability is visceral to those in Small Island Developing States (SIDS), Sub-Saharan Africa, Latin America, Eastern Europe and developing Asia, as a result of increasing fragility, migration, poverty and instances of natural disasters and conflict. As well as increasing instances of these events, the impact of natural disasters and economic disruptions tend to be more significant within emerging economies.
Challenging this through public finance sustainability requires two angles of attack: governments need to both mitigate the impact of crises, but also work to prevent them occurring in the first place.
Efforts to deliver the first focus on developing public finance resilience (fiscal space, revenue mobilization, value-for-money etc.). And prevention of future crises motivates development of infrastructure, and social public investment excellence (inclusivity, poverty reduction, “build back better” etc.).
In both cases, there needs to be a shared understanding of the goals of the reform. This alignment of goals is critical in embedding transformational change, such as the journey to accrual accounting or performance budgeting.
What is driving public finance sustainability momentum?
There are a range of factors driving public finance sustainability efforts around the world, including:
- recent crisis experiences and public finance impacts
- commitments and pressure to achieve the SDGs
- creation of sustainability in public finance practices and assessments:
- Climate e Gender Despesas públicas e responsabilidade financeira (PEFA)
- Climate Public Investment Management Assessment (PIMA)
- Sustentabilidade reporting for International Public Sector Accounting Standards (IPSAS).
How do governments deliver against sustainability objectives?
Como nós wrote in 2022, there are four areas of focus needed by governments if they wish to achieve sustainability and reduce the impact of crises. In each area, there is a need for both a PFM process adjustment e support from specific financial software (which we call planeamento de recursos governamentais (GRP)):
| Focus Area | PFM Requirement | GRP Enabler |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability planning and implementation | Multiple-year program and performance budgeting planning (incluindo o apoio aos ODS), integrated with public investment management processes | Chart of Accounts (budget classification) side tables with limited changes to core structures, integrated with medições de realizações e resultados em algo como uma Tabela de Objectivos. |
| Gestão do risco de sustentabilidade | Budget planning processes to build in factores de risco as a basis for monitoring and evaluation, with fiscal risk management consistent with the PEFA Indicador de desempenho 10 Comunicação de riscos fiscais | Support of “gestão do risco empresarial” structures in budget planning that integrates with monitoring and evaluation dashboards. |
| Sustentabilidade consumo de recursos | Use of activity-based costing approaches to track resources used, including carbon footprint, that can be leveraged through “cost drivers” in budget planning to forecast energy and carbon usage | Integration of processos orçamentais, de aquisição e contratuais para acompanhar os recursos consumidos pela modificação da oferta |
| Natural resources assets and liabilities | Use of accrual accounting including methods to value natural resource assets, while accounting for natural resource and contingent liabilities in areas such as extractives and agriculture | Leverage multiple-year budget preparation modelling tools, while moving towards accrual accounting, extending asset and property accounting to uncover the real value of a country |
How can an Integrated Financial Management Information System (IFMIS) help achieve sustainability goals in developing countries?
An effective IFMIS is essential in ensuring access to accurate, real-time data which enables robust and transparent financial management and service delivery.
FreeBalance provides the first global GRP solution, the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™, which is designed exclusively for PFM. This is important because governments have unique needs when it comes to budget planning, preparation, execution, and performance evaluation. Enterprise resource planning (ERP) tools aren’t developed for government contexts, and GRP is not the same as ERP.
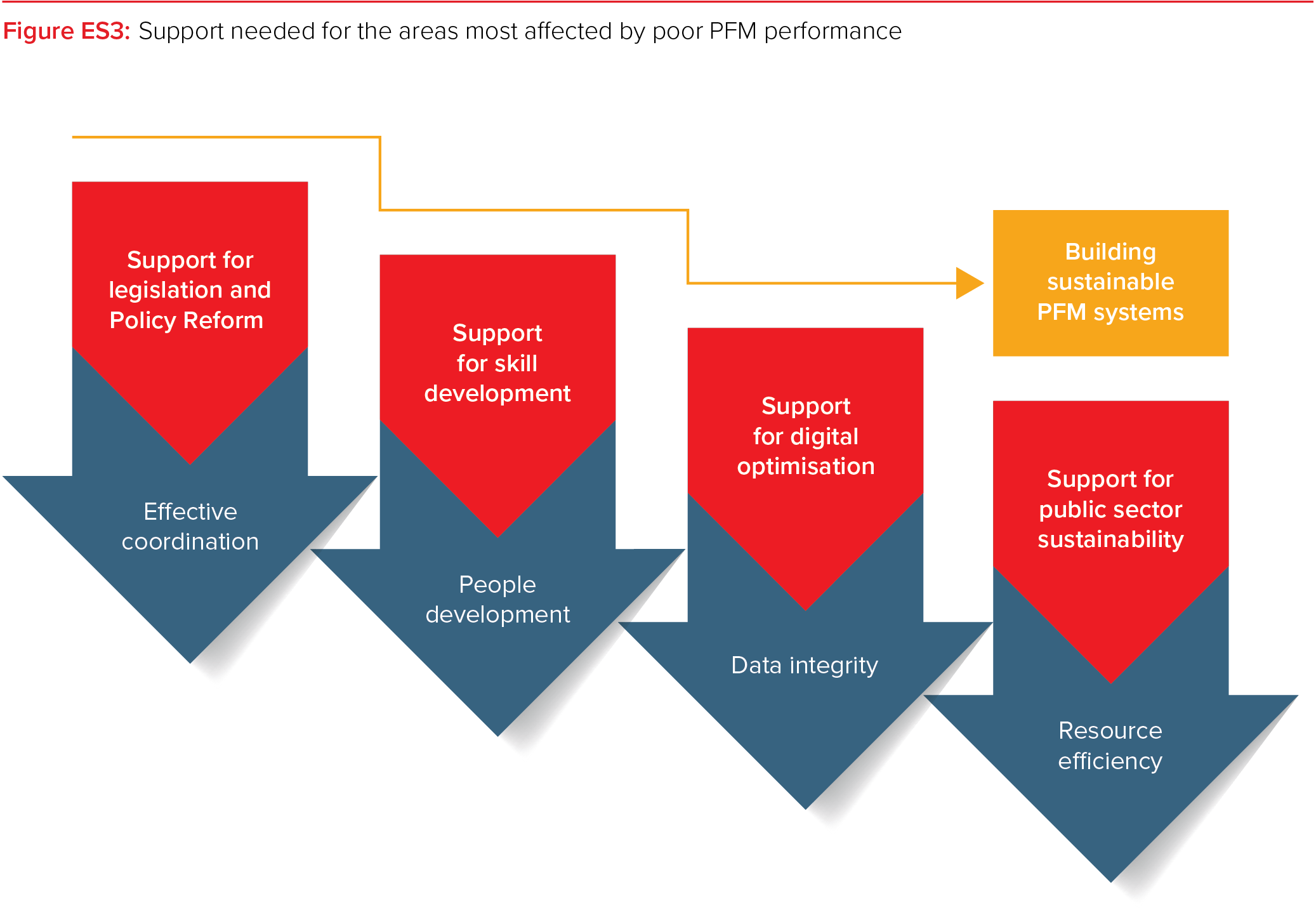
Leveraging our purpose-built government IFMIS in tandem with FreeBalance’s serviços de consultoria, enables governments to zone in on the areas identified by the ACCA as most in need of support (see diagram above):
Effective Coordination
The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ empowers effective coordination through:
- Compliance with legislative and policy frameworks
- The configuration of the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ ensures compliance with the legislative and policy requirements of sustainability efforts, while supporting key agencies mandates through program budgeting
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ provides real-time data for policymakers through interoperability, management alerts, and dashboards, and uses multiple-year Chart of Accounts as key fiscal metadata.
- Delivering performance assessment tools
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ offers integrated performance monitoring, by linking Charts of Accounts with Charts of Goals for output and outcome monitoring and reporting throughout the budget cycle
- Automated alerts and notifications, including via email and messaging systems, are built into the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ to ensure that any move away from expected performance is swiftly attended to.
- Enabling inter-agency collaboration
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ features secure data access security, using the Chart of Accounts to group and role definitions, and separation of data and business logic layers. This supports reporting, analytics and fiscal transparency
- Collaborative workspaces are fully supported by the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™, through task dashboards, low-code workflow management, and content management.
- Supporting stakeholder buy-in
- FreeBalance’s proprietary, ISO-9001:2015 certified agile implementation methodology, A-i3+qM, facilitates effective change management by focusing on gaining project authorizing environments, and government-specific change processes
- Stakeholders are assured of the benefits of PFM reforms via custom dashboards, scorecards and alerts for sector groups.
Data Integrity
Digital transformation relies on data integrity. FreeBalance helps governments to ensure the integrity of their data by utilizing:
- Impact-focused digital solutions
- FreeBalance conducts a needs assessment with each customer, using tools from our FreeBalance’s A-i3+qM methodology to analyze what a government needs from an IFMIS, comparing “systems of record” with systems of “engagement”, “intelligence” and “innovation”
- Our A-i3+qM methodology also helps governments through a modernization journey, covering digitization through digitalization to digital transformation.
- System integrations
- The underlying technology for the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ is a single open unificado platform: the FreeBalance Accountability Platform™. This ensures interoperability and simplifies integration to financial subsystems
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ provides a single point for metadata and controls management, ensuring a “single version of the truth” and compliance with government regulations.
- Ethical Integrated Artificial Intelligence
- Our A-i3+qM methodology supports organizations to define and implement AI governance and ethics
- The FreeBalance Accountability Platform™ features robust data security protocols. It does this through routing all queries via the business logic layer (with no exposure of business logic in browsers), good security practices, encryption and the integration with biometrics, public key encryption, network security analysis tools, firewalls, and virus protection.
- Up-skilling public professionals
- O Academia FreeBalance e training services provides capacity building, so that skills development goes beyond FreeBalance products to emerging technologies
- FreeBalance’s A-i3+qM methodology supports iterative training through workshops and training courses that supports government certification needs and continues learning.
Driving People Development
- Transition to accrual accounting
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ enables the move to accrual accounting through activação progressiva, taking governments on a journey from cash through modified cash and modified accrual, to full accrual accounting, meeting Normas Internacionais de Contabilidade do Sector Público (IPSAS)
- FreeBalance’s training services, alongside specialized courses from the FreeBalance Academy, improve skills in IPSAS cash management and IPSAS accrual compliance.
- Building capacity to promote sustainability
- Programs offered through the FreeBalance Academy help to integrate sustainability across government budget cycles
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ program and cost accounting functionality provides data visualization tools which demonstrate progress against social and infrastructure public investment goals, spending, and outcomes.
- Transferring and retaining skills
- Adaptable help, content and knowledge management tools within the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ enable building knowledge bases
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ função pública functions support training programs, succession, talent and career planning.
Improving Resource Efficiency
- Envolvimento das partes interessadas
- Automated portais de transparência are included within the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™. These enhance stakeholder engagement and public accountability around sustainability
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ integrates Charts of Accounts with Charts of Goals, enabling stakeholder analysis and feedback related to spending outputs and outcomes.
- Relação custo-benefício
- By integrating the Chart of Accounts with the Chart of Goals, the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ supports improved links between financial performance and strategic performance. Sustainability objectives are cascaded to value considerations used in budget, procurement, and public investment planning
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ gestão de contratos públicos supports sustainability in value calculations while supporting results reporting, enabling a focus on both procurement process compliance and effective investment.
- Internal controls and audit
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ has ESG-sensitive controlos das autorizaçõese valid code combinations can be configured to align with sustainability objectives
- Audit trails and audit management within the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ supports sustainability compliance and performance audit.
How can governments structure sustainability in PFM reform and financial management software?
O arquitectura de soluções technique aligns sustainability objectives to PFM reform and the financial management technologies supporting it. Changes to Integrated Financial Management Information Systems (IFMIS) is usually part of PFM reform.
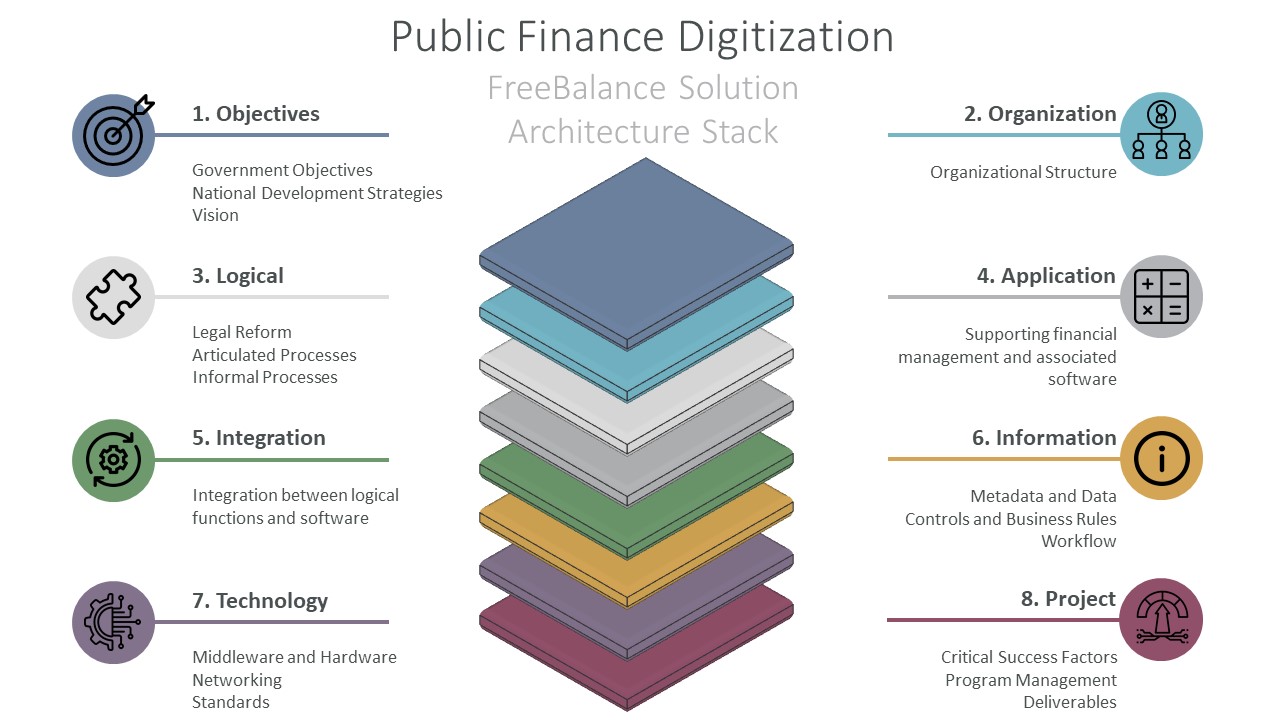
Objectivos Ver
- Government goals: government sustainability goals within visions, national strategies, pillars, and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) objectives
- Expected outcomes: sustainability targets set by governments, including references to relevant SDG targets and indicators.
Visão da organização
- Main stakeholders: line ministries and agencies who share sustainability programs
- Involved stakeholders: donors, oversight agencies, civil society, political parties, parliamentarians.
Visão lógica
- Core functionality: funções de gestão financeira tipicamente essenciais
- Major subsystems: tais como folhas de pagamento, activos, aquisições, dívidas, que devem ser integradas com os
- Functions supported: functions like audit, transparency, decision-making.
Vista da aplicação
- Core system: typically the core financial system, although could be more than one system
- Major subsystems: aplicações reais utilizadas, podem incluir o ambiente actual em contraste com o futuro
- Supported applications: supported by systems like portals, dashboards.
Vista de integração
- ParaOs sistemas aos quais os sistemas fornecem informações
- Deos sistemas para os quais o sistema recebe informações
- Tipo: the integration method like API, web services, RPC, flat file, database, ETL, screen scraping.
Visualização de informações
- Systems and subsystems: alinhado com a vista da aplicação
- Data migration: mostra os dados provenientes dos sistemas a substituir
- Information sources: for data, metadata, task management, controls, organizational structure.
Visão tecnológica
- Presentation layerinterfaces de utilizador a suportar
- Business logic layer: application servers, middleware, programming languages to be used
- Data layer: actual databases to be used.
Visualização do projecto
- Coordenar com uma única vista de projecto
- Identificar dependências dentro das vistas e entre vistas
- Alinhar projectos com os objectivos do governo, dos doadores, dos ministérios sectoriais e dos projectos
- Gerar planos de jogo, agile boards, and traditional project plans.
FreeBalance’s PFM experts work with customers to define how advanced GRP tools can support PFM reform and sustainability. Entre em contacto to find out how the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ can help your organization.
