Public Financial Management (PFM) plays a significant role in smart government. FreeBalance is developing numerous “vision cases” to describe the intersection of PFM and “smart”. The planning and implementation of smart cities is enabled through PFM techniques and the use of open government.
Education cannot become ‘smart education’ without citizen-centric technology. Smart city developments enable more engagement between the public (student, educators, government officials, etc.) and the technology itself. Smart public education is a combination of digital readiness and environmentally friendly buildings/institutions that are built with the interest of citizens in mind.
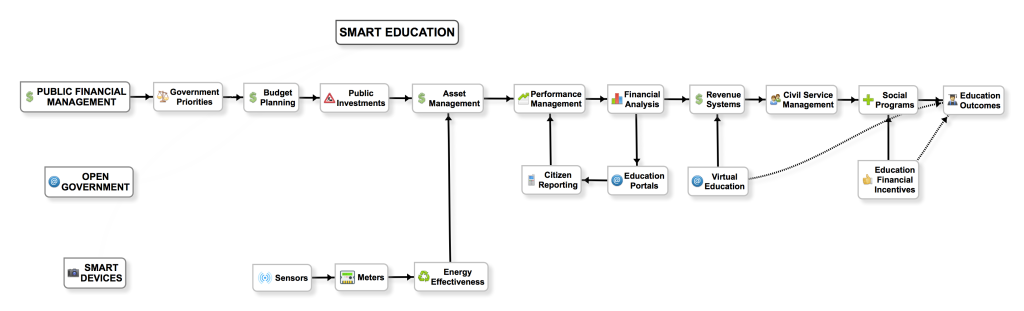
- Government Priorities: government priorities result in education budgets and public investments
- Asset Management: asset and property management systems for departments of education, schools, and universities which include geographic information, maintenance schedules, warranty, etc. These are core for traditional public institutions and services
- Smart Meters & Sensors: sensors on infrastructure and equipment (example: AC sensors, printer/computer sensors, light/energy sensors) track consumption and aim to conserve energy and save money for school districts and public infrastructure
- Citizen Reporting: this is enabled through camera and GPS functionality found in smart technology tools, such as tablets, phones and drones.
- Financial Analysis: costs for building ‘smart’ schools and investing in digital education services such as online learning and virtual classrooms
- Education Portals: displays level of digital readiness in schools across the region; displays amount of energy and consumption saved to promote environmentally friendly and sustainable schools
- Revenue Systems: show changes in education costs due to virtual learning and online educational programs, changes in costs associated with materials such as textbooks and access to free online courses for students who cannot afford formal education
- Payroll & Civil Service Management: adjusts records to account for talent management and payroll processing for online educators and service providers
- Incentives: use analysis to create incentive educational programs and rebates for certain specializations such as STEM learning, aligned to government priorities
- Education Outcomes: analysis of education outcomes based on investments and use of classroom and virtual training like distance learning and MOOCs
The integration of PFM, open government and digital devices provides the “smart” in Smart Government:
- Citizen-centric: engages civil society through education portals and sensors, and variety of educational learning platforms such as MOOCs
- Data-driven: maps out information collected from sensors with financial and revenue information with comparison of classroom and virtual education for outcomes
- Performance-focused: changes the learning behavior of students and disrupts traditional education conventions with the inclusion of online learning, coding camps, STEM learning, etc.
- Long-term: continually adjusts policy and costs/ revenue to reflect changes in education systems and enables experimentation
