Governments are struggling to keep up with the ever-growing demand for technology investments.
The pressure is on for governments to modernize and invest in new technologies, but it can be hard to know where to start or how to prioritize these investments. The practice of acquiring an Integrated Financial Management Information Systems (IFMIS) often begins with the context of private sector accounting or existing software in use. But financial management differs in the public sector which means that this approach often misleads prioritization.
FreeBalance PFM Component Map
To help governments FreeBalance has developed a PFM Component Map that enables the determination of functional needs and priorities for effective Public Financial Management. The FreeBalance PFM Component Map provides a high level view to government financial functions. It is a target for determining the characteristics of an IFMIS.
How Does the FreeBalance PFM Component Map Help Governments?
The FreeBalance PFM Component Map helps governments to identify which components are needed and their level of importance. Governments can also map current systems against the component map to determine gaps. It enables determining the required portfolio for automation, reform and improvement.
A component is a defined piece of functionality that could operate stand-alone. The FreeBalance PFM Component Map enables drilling into more levels of detail to identify rich functional requirements. It also provides components for transparency and citizen service. The arrangement and definition of components is government centric.
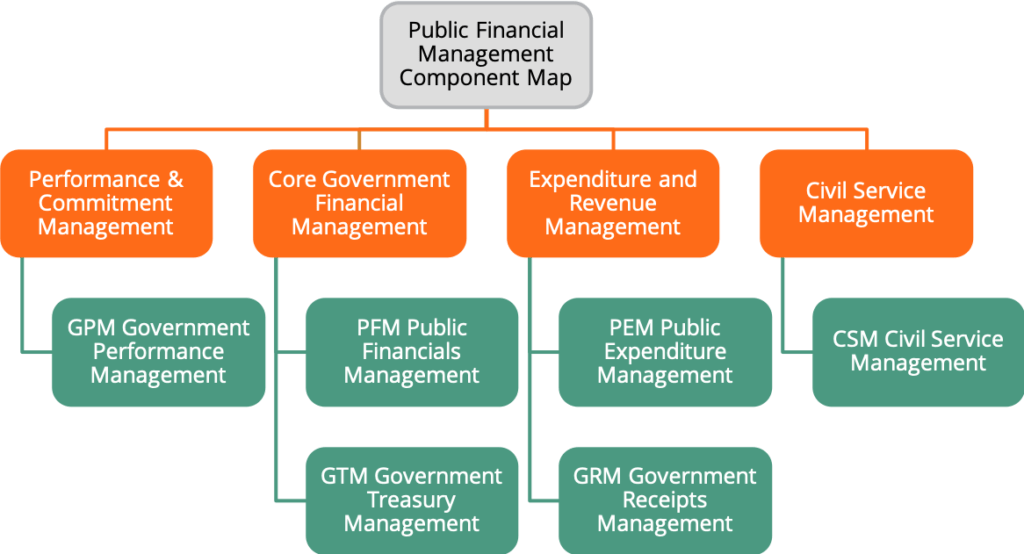
What are the Components of Public Financial Management?
The main functional components for the FreeBalance PFM Component Map are:
- Government Performance Management
- Budget planning / formulation
- Policy management
- Public accounting and budgetary classification
- Performance management
- Aid management and harmonization
- Commitment and Budget Accounting
- Budget and appropriation control
- Commitment and obligation control
- Budget execution and funds release
- Government Financial Management
- Reform and modernization activation
- (Treasury) General ledger
- Project accounting and management
- Assets and inventory management
- Treasury Management
- Cash management
- Debt and investment management
- Foreign exchange
- Public Expenditure Management
- Procurement
- Grants management
- Intergovernmental transfers
- Social benefits
- Payment management
- Government Receipts Management and Revenue Administration
- Non tax government revenue
- Taxation
- Civil Service Management
- Civil service reform
- Payroll and pensions
- Civil service workforce management
- Movement life
- Capacity management
- Benefits management
Conclusion
To find out how the FreeBalance PFM Component Map can help your government prioritize its technology investments, please get in touch.
