Government organizations have an ever-increasing need to foster meaningful relationships with a wide range of stakeholders. Systems of engagement emerged as a transformative force over the last decade, enabling governments to forge seamless connections with stakeholders, streamline financial processes, and enhance oversight capabilities. They have a key role to play in supporting governments to embrace digital solutions, and are a building block towards government digital transformation.
What are Systems of Engagement?
Systems of engagement are a type of information system designed specifically to facilitate two-way interactions between government organizations and their stakeholders. Effective communication and interaction, not only with internal audiences (employees) but also external audiences (such as citizens, businesses, the media and stakeholders within other public organizations), have become paramount for governments to most effectively manage public funds.
Systems of engagement can encompass a wide range of technologies, including mobile applications, social media platforms, cloud-based solutions, and real-time communication tools. These technologies can be used in a multitude of ways to enhance how staff and citizens interact with the government in matters related to financial management.
The term was first coined in the 2011 white paper “Systems of Engagement and the Future of Enterprise IT”, written by Geoffrey Moore. Since then, systems of engagement have become more prevalent and the concept has been built on further with the emergence of systems of intelligence and systems of innovation.
Key Characteristics of Systems of Engagement
Unlike traditional systems of record, which are primarily focused on ‘back office’ data storage and management, systems of engagement are for use in ‘frontline’ contexts. They prioritize real-time interactions and user engagement, empowering citizens, businesses, and government officials to collaborate, exchange information, and contribute to informed financial decisions.
Systems of engagement are characterized by several key features that distinguish them from traditional IT systems:
- Decentralized architecture: systems of engagement are not centralized repositories of data but rather decentralized systems that empower users to interact and collaborate based on their specific needs and roles
- Real-time data exchange: systems of engagement facilitate the exchange of real-time data, enabling organizations to gain immediate insights and make informed decisions in the moment
- User-centric design: At the heart of a good system of engagement lies a user-centric philosophy. They facilitate engagement and collaboration among employees, customers, partners, and other stakeholders, and prioritize accessibility, usability, and a seamless user experience. This all promotes transparency, and accountability in the management of public finances.
- Mobile-enabled capabilities: systems of engagement recognize the increasingly mobile workforce and provide access to tools and information from anywhere, at any time.
The Benefits of Systems of Engagement for Governments
In the public sector, systems of engagement can play a transformative role in improving citizen engagement, enhancing government transparency, and streamlining public services. For instance, systems of engagement can:
- Engage citizens in policy making: systems of engagement can provide platforms for citizens to participate in policy discussions, providing valuable feedback and shaping government decisions
- Enhance government transparency: systems of engagement can make government data and information more accessible to citizens, fostering trust and accountability
- Streamline public services: systems of engagement can facilitate online applications, appointment scheduling, and document sharing, reducing bureaucracy and improving the citizen experience
- Improve collaboration among public agencies: systems of engagement can break down silos between government agencies, enabling seamless information sharing and coordinated service delivery.
When it comes to public financial management specifically, the user-centric, interactive focus of systems of engagement helps to increase transparency in government finances, making it easier for citizens to understand how their tax dollars are being spent. This, in turn, fosters greater accountability from government officials and builds public trust.
The implementation of a system of engagement for PFM can yield a myriad of benefits for governments, including:
- Enhanced transparency and accountability: PFM systems of engagement break down silos and foster open communication channels, enabling seamless access to financial information for citizens, businesses, and other stakeholders
- Improved citizen engagement: PFM systems of engagement provide platforms for citizens to participate in the budget process, offer feedback on financial policies, and track the allocation of public funds
- Strengthened oversight and audit: PFM systems of engagement make it easier for external actors, such as legislatures and audit agencies, to conduct more effective oversight of government finances, detecting potential irregularities and ensuring proper use of public funds
- Streamlined financial processes: PFM systems of engagement automate tasks, provide real-time data, and streamline communication channels, making financial processes more efficient and less prone to errors
- Data-driven decision-making: PFM systems of engagement gather, analyze, and present financial data in a user-friendly manner, enabling government officials to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
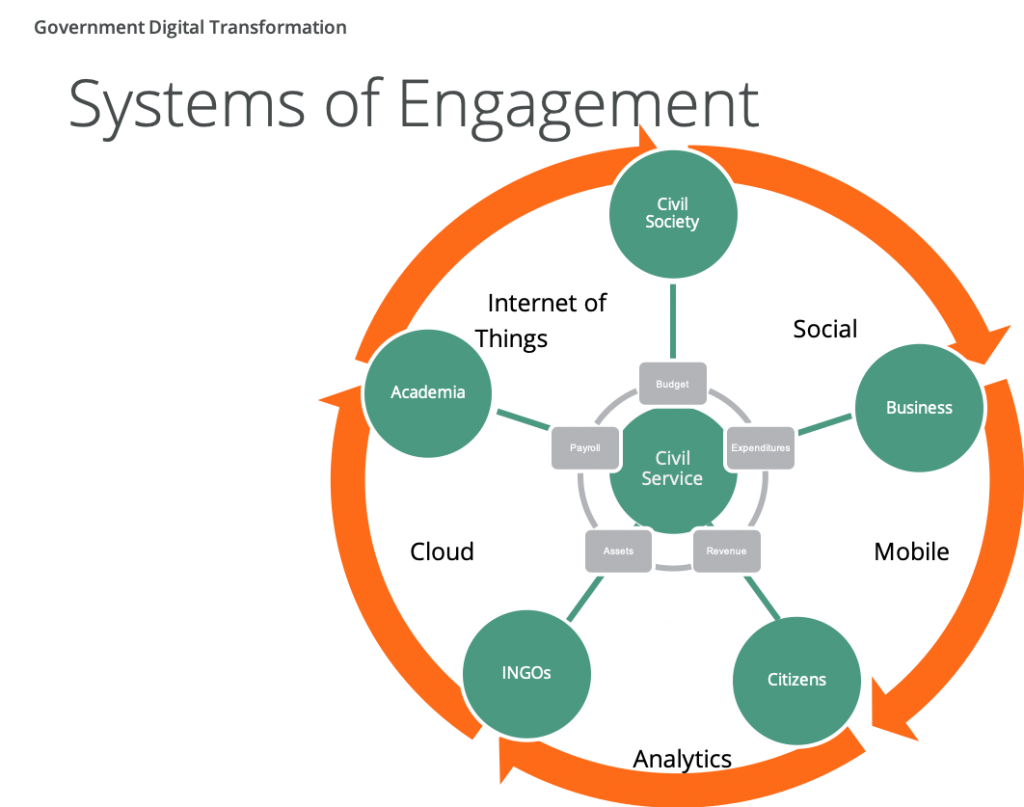
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Systems of Engagement in Public Financial Management Settings
While systems of engagement offer significant benefits, there are some challenges which governments need to consider. Firstly, just like systems of record, systems of engagement handle complex and sensitive data, so security protocols need to be robust. Secondly, systems of engagement overlay and complement systems of record, and may rely on other systems to work well. Integration with other existing systems needs to be smooth to ensure a seamless flow of data, avoid data silos and ensure a unified user experience; it isn’t just about the new system, but how it interacts with, supports and is supported by other systems.
Humans are one of the biggest factors in any IT system implementation. Moving to a system of engagement within PFM will likely require a change not just in departmental processes, but also in organizational culture. Governments need to develop a comprehensive change management plan to communicate the benefits of the new systems, address concerns of stakeholders, and provide adequate training and support. And lastly, plans for sustainability and maintenance need to be agreed upfront. Ensuring the long-term sustainability and maintenance of a PFM system of engagement is crucial to its success. Governments need to allocate adequate resources for ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and support to ensure that the systems remain effective and up-to-date.
PFM Systems of Engagement in Practice
Systems of engagement are at the heart of a number of modern government strategies, including smart government, open government and collaborative resource planning.
In each case, the system of engagement which enables these approaches relies on an effective government resource planning (GRP) solution, such as the FreeBalance Accountability SuiteTM:
- Smart government and smart city technologies leverage GRP transaction data, records management “unstructured” data, software logs, Internet of Things (IoT) devices and email, text and social media feeds. While these are met with excitement, some pilots have not been able to scale successfully because they were lacking an effective underlying GRP solution
- Open data transparency and engagement technologies have failed to live up to their initial promise, because most initiatives were based on one-way communications from the government to citizens. This changes when information sharing is facilitated by an accurate and user-friendly GRP tool, and engagement is two-way
- GRP systems and subsystems were originally developed to improve transaction processing, however they offer the opportunity to create increased efficiency when used collaboratively in context. The GRP isn’t for use in isolation: users need access to knowledge systems, to policies and procedures, and to “just-in-time” learning systems. They need to interact with colleagues to complete transactions. And, the scope of transaction collaboration increases with open government mechanisms. For example, the workflow of a vendor question during an eProcurement cycle benefits from front and back-office integration.
The FreeBalance Accountability SuiteTM is specifically designed for governments. It offers a range of government resource planning solutions which support a systems of engagement approach across the entire budget cycle.
For example, the FreeBalance (PFM) Public Financials Management tool enables governments to publish statutory financial reports online quickly and easily. (GTM) Government Treasury Management provides compliance reporting functionality and (CSM) Civil Service Management delivers interactive recruitment, shortlisting and onboarding tools to ensure the best staff are hired and retained.
Conclusion
By embracing systems of engagement, governments can bridge the divide between their internal operations and their employees, citizens and stakeholders. PFM systems of engagement help to foster meaningful connections, enhance collaboration, and ensure governments become more citizen-centric, transparent, and responsive to the needs of the communities they serve.
Find out more about how the FreeBalance Accountability SuiteTM can meet your systems of record needs, set up a call with our PFM experts.