What is Fiscal Decentralization?
Fiscal decentralization is about moving the responsibility for expenditures and/or revenues to lower levels of government. If local governments have to execute decentralized functions effectively, they must have an adequate level of revenues as well as the authority to make decisions about expenditures. And any decentralization program must cover the most critical elements of public expenditure, namely fiscal sustainability, efficient resource allocation, operational efficiency and transparency.
Properly implemented fiscal decentralization improves service delivery in that public servants who understand the local context are empowered to make sound decisions across the budget cycle based on reliable, real time financial information. A program of government fiscal decentralization must include:
- Progressive activation of functionality to local and regional governments in line with capacity improvements and legal reform
- Optimization of the full budget cycle beyond accounting
- Inclusion of decentralization to line ministries, agencies, and State-Owned Enterprises
Why is Fiscal Decentralization Important?
Because Fiscal Decentralization Improves Public Finance Effectiveness
Government operational and fiscal decentralization leads to improved local decision-making, infrastructure development and service delivery, however, many countries struggle to achieve the benefits of decentralization, delegation, and devolution. Challenges include accountability, capacity, coordination, discretion, technology, and variability.
In our experience from working in countries such as Kosovo, Mongolia, Sierra Leone, Liberia and Timor-Leste, we have seen that the improvements flowing from a successful fiscal decentralization program only accrue when there is high quality governance in the decentralized agencies of the national and sub-national governments. Especially when there are high levels of accountability within the sub-national governments (SNGs) and integrated financial rules between the national government and the decentralized agencies.
Because Sub National Governments Manage Significant Funds
- According to an OECD report sub national governments in OECD countries account for 40% of public expenditure, corresponding to 16% of GDP, a proportion that has increased in recent decades for most countries
- A report to the Global Observatory of Local Finances showed that the global average for SNGs is around one-quarter of total government spending or 9% of GDP. Sub national spending shares are particularly high, exceeding 35% of government spending and 15% of GDP in most federations but also in some unitary countries
- The same report also showed that service delivery is critical for SNGs with the bulk of their spending on education, general public services and social protection
Issues Associated With Fiscal Decentralization
There are both a number of misconceptions and some real issues with fiscal decentralization. The most common ones we have encountered include:
Misconceptions
- Give local or regional governments very simple solutions, even Excel-based, because there is insufficient human capacity
- Limit budget planning and commitment accounting functionality, also because of insufficient human capacity
- Decentralization is only a local and regional government concern, and does not relate to national governments
Issues
It must be remembered that fiscal decentralization varies among countries, and within countries.
- A different approach is required for federal vs. unitary types of government
- Some countries have special economic zones and indigenous governance zones which affect how decentralization programs are rolled out
- The footprint of State-Owned Enterprises and the extent of privatization and process outsourcing also has an impact
- And while poor local or regional capacity should not be assumed, there are at times valid concerns around urban and rural governance capabilities
Fiscal Decentralization and Corruption
There is of course the risk of increased corruption at the local level. Which is why it is important that any decentralization program includes the implementation of a government resource planning system such as the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ with:
- Robust expenditure and segregation of duties control
- Fully auditable transactions
- Automated processes to eliminate many points of corruption
- Data integrity and encryption to trap attempts to manipulate data
- Password challenge and other techniques to enforce segregation of duties
- Automated fiscal transparency support
How Does FreeBalance Help Fiscal Decentralization?
We see decentralization as 1 of 4 progressive activation themes for PFM reform which we approach sequentially.
At FreeBalance we believe in progressively activating functionality enhancements based on improved capacity over time. In addition, we use configurable software to support the unique requirements of decentralization rather than code customization. We also help customer governments to standardize and consolidate national accounts through an adaptable Chart of Accounts and Chart of Goals which benefits decision making and goal setting. The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ enables all revenue and expenditure sources, not just budgets provided via the national government, to provide comprehensive Public Financial Management (PFM) at all levels of government. And it adapts the discretion and accountability mix in line with reform and capacity building.
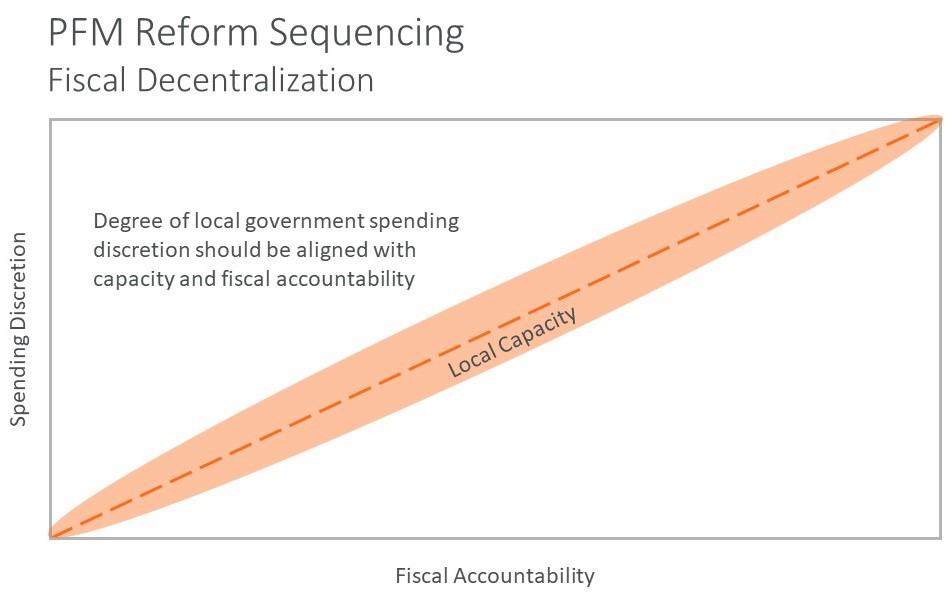
Effective fiscal decentralization requires balancing discretion with accountability in line with capacity improvements. Increasing civil service accountability without enabling local decision making creates perverse incentives – as does providing local decision making discretion without accountability.
The bottom line is that fiscal decentralization is effective when it is aligned to a country needs, adapts to constitutional and capacity constraints, supports available bandwidth and enables the entire budget cycle.
Unique FreeBalance Approach to Fiscal Decentralization
With almost 40 years of ‘in the field’ experience, FreeBalance has perfected it’s approach to fiscal decentralization with a number of unique differentiators:
- Technology:
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ has a unified postmodern design that supports both national and sub national integration
- Deployment:
- Our deployment model supports on premise, hosted, public / private clouds, shared services, SAAS and disaster recovery
- Configuration:
- Our no-code/low-code approach as primary method for adaptation supports progressive activation making fiscal decentralization reform over time sustainable
- Autonomy:
- The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ provides sub national levels of government with a fully integrated financial management system so that decision making can be devolved as well as revenue collection and expenditure.
The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ has also been leveraged to support other forms of legal reform in concert with fiscal decentralization such as:
- Migration to accrual accounting
- Development of more advanced audit
- Program budgeting, Medium-Term Expenditure Frameworks, and performance management
- Fiscal transparency and transparency portals
