What is Government Resource Planning?
Governments have unique and special requirements that are different from the private sector.
Private enterprise-sized companies use Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software which helps run many if not all of its departments, ranging from purchasing, inventory, account management, human resources, and more. However, private companies are driven by profit. Governments are driven by their budget.
Government Resource Planning (GRP) is much more than a variation of ERP software: it’s a unique tool for financial and information management that allows and enables a government to build capacity, increase self-sufficiency, improve transparency, and ensure accountability. The result is a government that is trusted, both by its citizens and funders such as the World Bank and International Monetary Fund (IMF), etc.
Governments purchase GRP systems such as the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ to improve fiscal transparency, efficiencies and outcomes. Unlike the private sector, the government “bottom line” is not profitability – it’s delivering citizen services, improving prosperity and ensuring a sustainable and equitable future for the country.

Features and Benefits of Government Resource Planning
GRP is software designed for the unique requirements of Public Financial Management (PFM). GRP software is budget-driven through the use of Commitment Accounting, where the budget is the legal embodiment of government objectives. Commitment Accounting is used only in government and other forms of PFM.

GRP is designed to cover the entire government budget cycle, including budget preparation and budget execution. Budget preparation is the key mechanism for governments to determine how objectives will be met and how to improve government performance.

Government revenue and expenditures are managed during budget execution using Commitment Accounting. Funds are set aside during procurement and hiring cycles to ensure that the budget is not exceeded.

Changes in the government’s financial situation results in budget transfers to ensure fiscal discipline.

All of the above needs to be executed in line the government’s fiscal risk rules and meeting the requirements of Treasury such as bank reconciliation and cash, debt and investments management.

And the component that so many people consider to be the same in the private and public sector – human resources – is in fact very different in government. Civil Service Management is far more complex because governments often have a huge workforce, with many layers of hierarchy and complicated payroll rules.

Government Resource Planning and Public Financial Management
Many observers argue that governments should operate more like businesses (notwithstanding the current financial crisis). And the discussion about Public Financial Management (PFM) can often be dominated by terminology from the private sector: “business rules”, “business process”, and “lines of business”.
It is true that there are some similarities in financial and human resource management between the public and private sectors. For example, all modern accounting systems use ledgers and journals. Yet, significant differences remain. Governments have very specific needs and public financial management is different to finance in the private sector.
How is Government Different from the Private Sector?
Governments can leverage lessons learned from the private sector, but the mission of governments differs from companies’ in many ways:
- Governments focus on mission effectiveness and outcome results. Companies focus on competitiveness and profit.
- Governments strive for accessibility to all citizens. Companies focus on one or more target markets.
- Government priorities are set through the legislative process. Company priorities are set by managers and shareholders.
- Governments strive for standardization across government entities. Companies strive for differentiation.
Components of Public Financial Management
FreeBalance has developed a PFM Component Map that enables governments to effectively determine functional needs and priorities. The FreeBalance PFM Component Map provides a high level view to government financial functions. It is a target for determining the characteristics of a GRP. Governments can identify which components are needed and the level of importance, and map against current systems against to determine gaps. It enables determining the required portfolio for automation, reform and improvement.
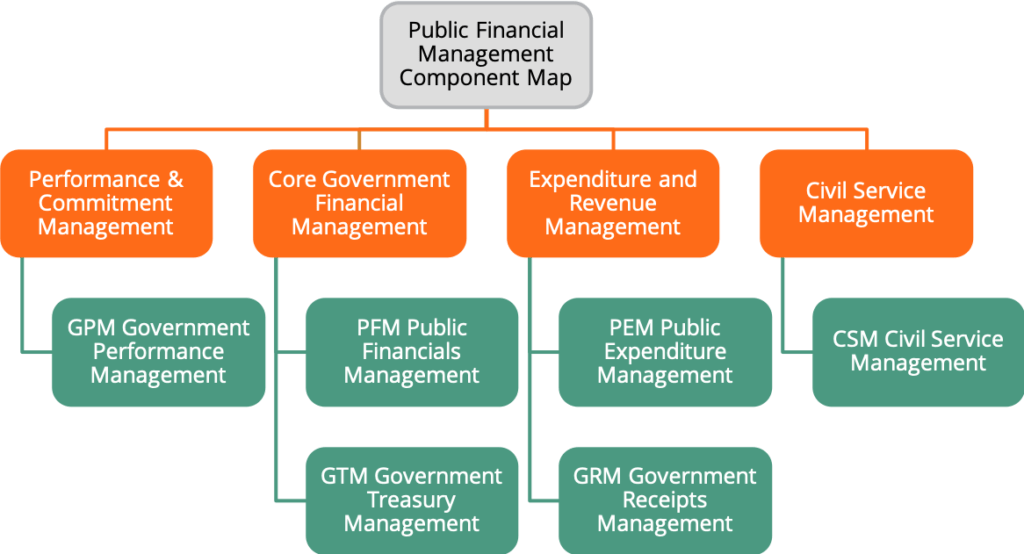
A component is a defined piece of functionality that could operate stand-alone. The FreeBalance PFM Component Map enables drilling into more levels of detail to identify rich functional requirements. It also provides components for transparency and citizen service. The arrangement and definition of components is government centric.
The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™
The FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ is a commercial off-the-shelf (COTS), GRP solution that covers the entire budget cycle and manages all critical government fiscal systems.
To find out more about how a Government Resource Planning solution such as the FreeBalance Accountability Suite™ could help drive Public Financial Management reform in your country, please get in touch.