What can we learn from resilience “wake-up” calls: pandemics, natural disasters, wars, food insecurity, and climate risks? For one thing, the term “resilience” has risen to top-of-mind among government leaders.
This is the first of three postings on resilience and public financial management:
- What is the heart of country resilience?
- Why is Public Financial Management the brain of resilience?
- How can governments transform country resilience?
What Do Leaders Mean by “Resilience”?
Among resilience concepts are:
- Climate resilience: climate mitigation, climate adaptation, and “build back better”
- Natural disaster resilience: emergency preparedness and rapid reaction
- Government financial resilience: counter-cyclical spending, fiscal space, and early warning for emerging fiscal crises
- Financial sector resilience: financial system leverage and coverage
- Cyber resilience: hacking, infrastructure redundancy, and cyberattack capabilities
- Wellbeing resilience: poverty reduction, inclusion, and social cohesion
As we noted in early 2021, it’s a VUCA world: volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity. That doesn’t mean completely unpredictable: something that we can’t plan for. The pandemic was not a black swan event in that events of this nature have long been predicted.
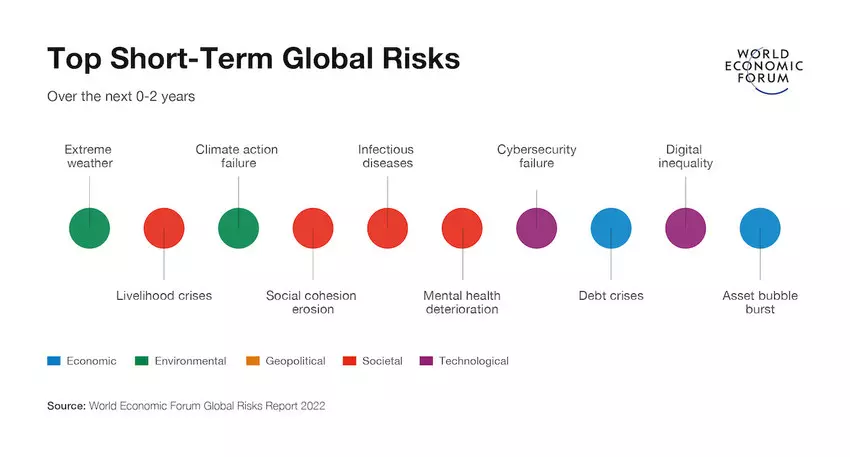
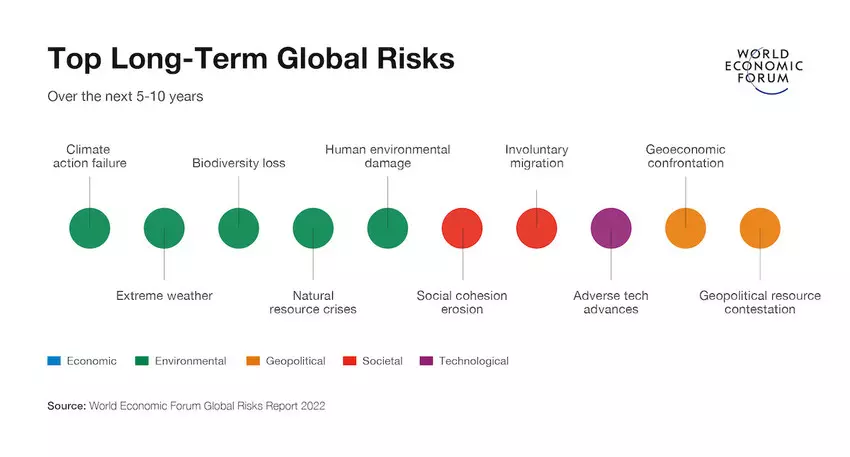
The potential severity of risks over the next 10 years has also been analyzed for 2022:

There you have it: economic, environmental, geopolitical, societal, and technological risks. These categories echo the standard business strategic planning concept: PESTEL (political, economic, societal, technology, environmental, legal).
Resilience For Whom?
Who is at the centre of PESTEL and global risks? The end point of the resilience supply chain? Beneficiaries? And, potential victims or risks?
People. Citizens.
Citizens are at the heart of resilience. We need to take citizens’ perspective on resilience. And, sustainability. That’s why we need to put citizen wellbeing for resilience policy prioritization regardless of how we define resilience. In other words, wellbeing resilience – poverty reduction, inclusion, and social cohesion:
- Climate resilience: extent to which climate affects the most vulnerable citizens for poverty reduction and inclusion
- Natural disaster resilience: extent to which governments can assist citizens in overcoming negative impacts of natural disasters quickly and effectively
- Government financial resilience: extent to which governments have the fiscal space and public finance efficiency to provide social protection and public investments during fiscal crisis
- Financial sector resilience: extent to which financial inclusion is supported during financial shocks
- Cyber resilience: extent to which important government citizen service delivery is supported during cyber attacks and digital infrastructure problems